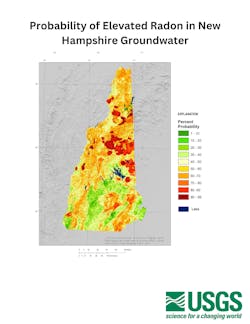
A recent study by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) finds that more than half of New Hampshire is underlain by groundwater that has a 50% or higher probability of having elevated levels of radon.
The research also finds that a small portion of the state’s groundwater has elevated concentrations of uranium.
The USGS says that this is the most comprehensive study to date and the first to create detailed statewide maps on the probability for any location in New Hampshire to have groundwater with either of those two radioactive elements.
The USGS estimates that 55% of the state is more likely than not to have elevated radon in groundwater. For uranium, 7% of the groundwater samples in the study were at elevated levels.
Much of the White Mountain region in the northcentral part of the state has relatively high probabilities for radon and uranium. Lower levels were found across parts of southern regions of the state.
“This is the first study to look across New Hampshire and estimate the likelihood of encountering radon or uranium in groundwater, helping identify who is living in an area with potential impacts to well water quality,” said Richard Moore, USGS hydrologist and the lead author of the new study.
“The process of where and how groundwater moves varies across the state and is influenced by factors such as regional geology,” continued Moore. “This study applies a comprehensive dataset to understand potential transportation of radon and uranium in different settings, allowing us to produce location-specific estimates for both elements.”
The New Hampshire state government’s standard for radon in drinking water is 2,000 picocuries per liter. The New Hampshire and EPA standard for uranium in drinking water is 30 micrograms per liter.
The research builds upon a previous USGS study in 2004 on radon in the state’s groundwater. The recently published study looks at both radon and uranium, includes more samples, uses a new methodology for statistical analysis and assesses more factors within the groundwater system such as bedrock types.
Both radon and uranium can be a concern to human health in communities that have private wells. Approximately 40% of New Hampshire residents rely on private wells for uses such as drinking water, and those wells are supplied by groundwater.
Notably, the recent study represents groundwater and not necessarily drinking water, as groundwater can be filtered or treated prior to becoming drinking water. USGS scientists investigated where the substances, which are naturally occurring, may exist and in some cases be elevated above safe drinking water levels.
The EPA regulates public water supplies, but maintenance, testing and treatment of private water supplies are the responsibility of the homeowner. Unless wells are tested, there’s no way to confirm the presence or absence of these contaminants. Residents interested in testing their private wells for radon and uranium can find more information on the New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services website.
The study is available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/1752-1688.13075.